Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) have revolutionized automotive safety, creating a safer driving environment by integrating automated systems and early warning mechanisms. Designed to enhance driver awareness and reaction times, ADAS uses sophisticated technologies, including human-machine interfaces, that adapt to potential traffic hazards. Whether built-in or added aftermarket, ADAS systems address the prevalent issue of human error, which contributes to the majority of road accidents. This article will delve into the components, challenges, and advancements in ADAS, as well as its unique application in emerging markets like India.
What is ADAS and How Does It Improve Road Safety?
ADAS technology aims to mitigate traffic accidents by providing advanced, automated safety features that reduce human errors on the road. The system leverages a network of sensors, microcontrollers, and warning systems to monitor road conditions and deliver essential safety alerts to the driver. With real-time updates on traffic congestion, roadblocks, and driver performance, ADAS technology enhances the driver’s ability to manage potential hazards effectively.
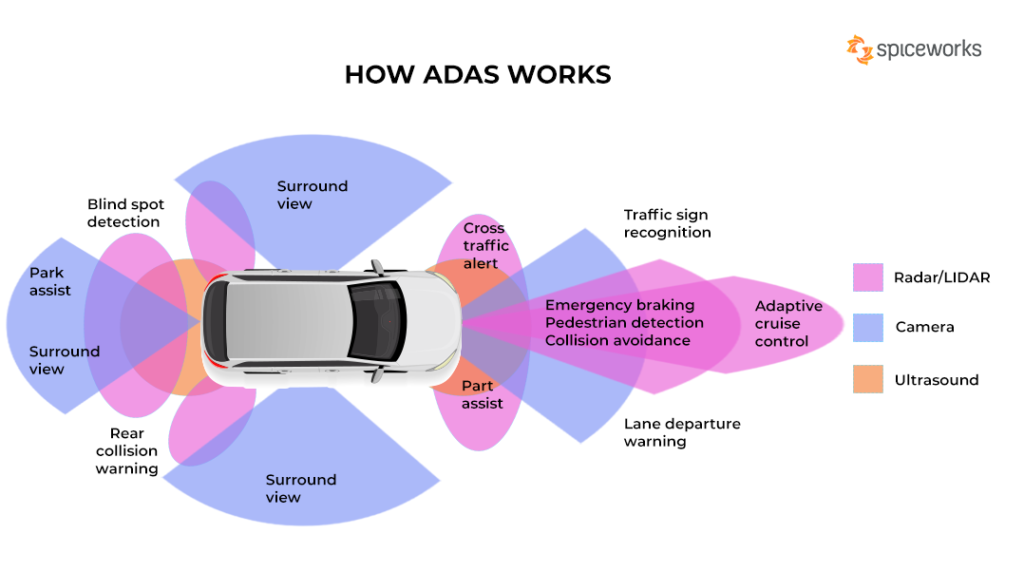
These systems support the driver in tasks that range from simple maneuvers, such as cruise control, to complex actions, including lane changes and parking. ADAS can also detect driver fatigue and distractions, which are leading causes of road incidents. With features like automatic emergency braking (AEB), adaptive cruise control (ACC), and lane-keeping assistance, ADAS significantly reduces the likelihood of accidents by ensuring faster responses to potential dangers.
Key ADAS Safety Features Transforming Modern Vehicles
Automotive safety has evolved significantly with technological advancements, making previously optional ADAS features standard in many vehicles. Key features include:
Adaptive Cruise Control (ACC)
ACC enables vehicles to maintain a safe following distance from the car ahead by automatically adjusting speed. Using radar and cameras, ACC ensures consistent speed adjustments, reducing the risk of rear-end collisions in stop-and-go traffic.
Anti-Lock Brake Systems (ABS)
ABS prevents the wheels from locking up during sudden braking, allowing the driver to maintain steering control. This essential feature is crucial for avoiding skidding on wet or slippery roads, enhancing vehicle stability.
Forward Collision Warning (FCW)
FCW systems alert the driver of a potential front-end collision by using sensors that monitor the road ahead. By providing timely alerts, FCW minimizes the likelihood of crashes and gives drivers crucial seconds to react.
High Beam Assist (HBA)
HBA automatically switches between high and low beams depending on surrounding light conditions and oncoming traffic. This feature improves nighttime visibility while minimizing glare for other drivers.
Lane Departure Warning (LDW)
LDW detects unintentional lane drifts and alerts the driver to take corrective action. By utilizing a front-facing camera, the system recognizes lane markings and warns the driver if the vehicle strays without signaling.
These ADAS features rely on a combination of cameras, radar, and light detection and ranging (LIDAR) systems, which work together to create a comprehensive view of the vehicle’s surroundings.
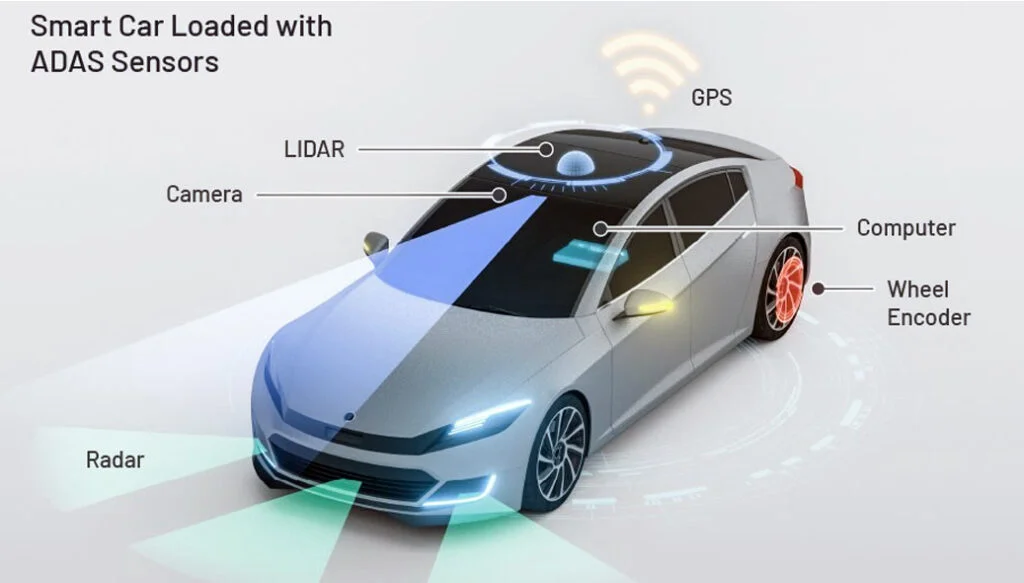
The Rising Demand for ADAS and the Push for Safety Regulations
Global automotive safety regulations have become a key driver for ADAS adoption. Many countries now mandate safety standards, such as AEB and ACC, to reduce fatalities and injuries caused by traffic incidents. Luxury car manufacturers have also accelerated the integration of ADAS as a standard feature, setting a benchmark that influences the wider automotive industry.
The implementation of these systems is supported by government initiatives to encourage safer roads. For instance, the European Union and the United States have enacted laws requiring certain ADAS components in new vehicles. As the demand for safer vehicles increases, ADAS technology is expected to become even more widespread.
Challenges Facing the ADAS Market
Despite the benefits, the ADAS industry faces several obstacles:
High Costs of ADAS Components
The cost of advanced sensors, such as radar and LIDAR, significantly impacts the affordability of ADAS systems. For instance, radar sensors used in AEB and ACC systems can cost upwards of $900, while rear radar sensors for blind-spot detection and cross-traffic alerts may exceed $2,000. The expense of these systems creates a barrier to adoption, especially in price-sensitive markets.
Maintenance and Repair Expenses
Maintaining ADAS systems can be costly, as sensor recalibration requires specialized skills and equipment. Due to the intricate nature of the technology, repairs often involve expensive parts and labor, adding to the overall cost of ownership.
Limited Availability of Skilled Technicians
The deployment and maintenance of ADAS technology require qualified technicians with expertise in automotive electronics and sensor calibration. In many regions, particularly emerging markets, the shortage of skilled professionals restricts ADAS adoption and operational efficiency.
Infrastructure Compatibility
ADAS systems depend on well-maintained infrastructure, such as clearly marked lanes and traffic signals. In developing regions, inconsistent road quality and limited infrastructure can hamper the effectiveness of ADAS features like lane departure warnings and ACC.
Challenges for ADAS Adoption on Indian Roads
India presents a unique case for ADAS technology. The country’s road conditions, which are often chaotic and unpredictable, pose additional challenges:
Unstructured Traffic and Obstacles
Indian roads are frequently crowded with pedestrians, stray animals, and irregularly marked lanes. Such conditions can confuse ADAS sensors, resulting in inaccurate hazard detection. For instance, an AEB system may respond to an animal on the road by braking abruptly, increasing the risk of rear-end collisions in heavy traffic.
Inconsistent Lane Markings
Many roads in India lack proper lane markings, making it difficult for lane-keeping assist features to function accurately. As a result, ADAS features such as lane departure warning can be less effective, leading to frequent false alarms that may frustrate drivers.
Infrastructure Gaps
The infrastructure required for ADAS functionality—such as consistent road signage and lane demarcations—is limited in rural areas and on certain urban roads. These gaps restrict the efficiency of ADAS and deter drivers from fully utilizing the system’s benefits.
Indian Government Initiatives to Foster ADAS Adoption
The Indian government has launched several initiatives to improve vehicle safety standards and promote ADAS technology. The Bharat New Vehicle Safety Assessment Program (BNVSAP), for example, sets safety benchmarks for new vehicles, including ADAS features. Additionally, the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) program offers incentives for electric vehicle (EV) adoption, encouraging automakers to integrate safety features aligned with ADAS technology.
These initiatives indicate a shift towards prioritizing road safety and technological integration. As ADAS adoption grows in India, further regulatory support and infrastructure improvements will be essential to overcome current challenges.
The Future of ADAS and Enhanced Road Safety
The development of ADAS technologies represents a pivotal step towards reducing road accidents and saving lives. As automation in driving becomes more sophisticated, future ADAS systems are likely to include more robust artificial intelligence algorithms, real-time data sharing, and connected vehicle technology. These advancements will improve the precision and responsiveness of ADAS, making roads safer for everyone.
Emerging Trends in ADAS Technology
- Automotive Ethernet: This high-speed communication protocol enables faster data transfer between ADAS components, enhancing real-time processing capabilities.
- Enhanced Human-Machine Interfaces (HMI): Future ADAS systems will offer more intuitive driver interactions, facilitating easier access to information and seamless control over automated functions.
- High-Definition Cameras and Improved LIDAR: As these technologies advance, the accuracy of ADAS in identifying obstacles and road conditions will increase, even in low-visibility scenarios.
As global automotive standards continue to evolve, ADAS technology will become increasingly prevalent, paving the way for safer roads and reducing the frequency of human-error-induced accidents.
